Does the Universe expand by stretching or creating space?
🌈 Abstract
The article discusses the expansion of the universe and whether it occurs through the stretching of space or the creation of new space.
🙋 Q&A
[01] Does the Universe expand by stretching or creating space?
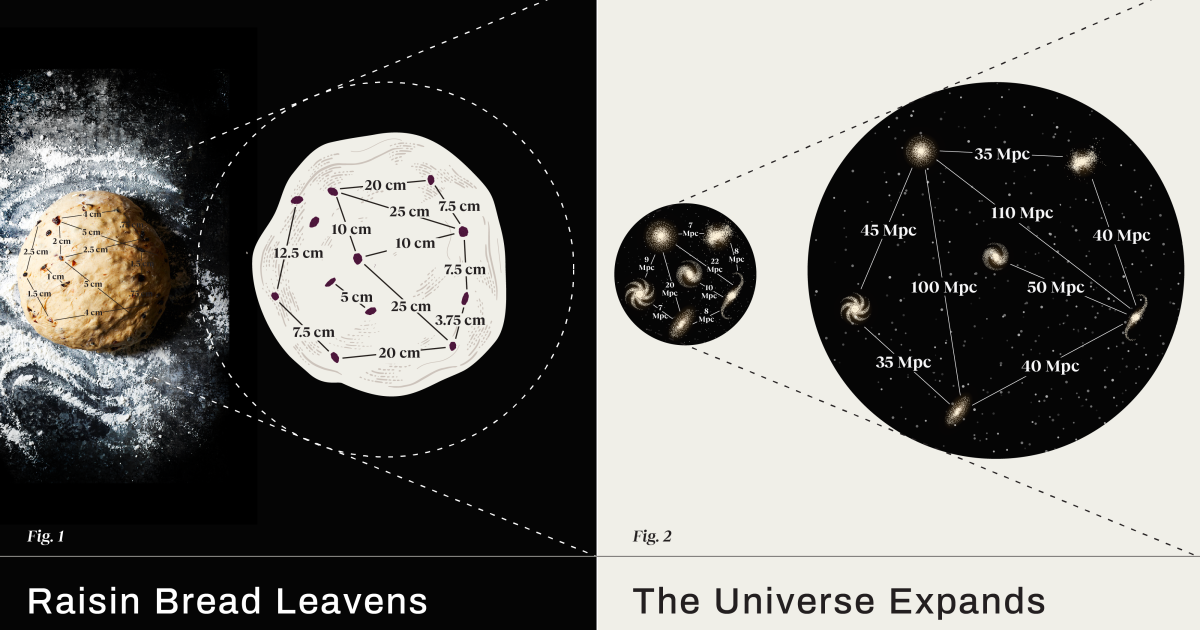
- The expansion of the universe can be interpreted in two ways:
- Space is stretching, causing light, gravitational waves, and other signals to be lengthened and redshifted as they travel through the expanding space.
- New space is being created, filling in the "gaps" opened up by the cosmic expansion.
- Both interpretations have their usefulness, but they are fundamentally limited analogies that can fail if used incorrectly.
- The expansion of the universe is real, but no single analogy perfectly captures the underlying physics.
[02] What is the relationship between the content of the universe and the expansion of space?
- General relativity relates the amount, distribution, and types of energy in the universe to the geometry and evolution of spacetime.
- In a completely empty universe, space would be flat and static.
- With a single point mass, space would be curved according to the Schwarzschild metric, but still static.
- However, when the universe is uniformly filled with matter, radiation, and other forms of energy, general relativity mandates that the universe must expand or contract over time.
- The Friedmann equations describe this evolution of the expanding or contracting universe.
[03] How do we observe the expansion of the universe?
- We cannot directly measure or experiment on space itself. Instead, we observe the effects of an expanding universe on measurable quantities like the redshift of light from distant galaxies.
- As the universe expands, the density of matter decreases, while the wavelength of radiation increases (redshift).
- Measurements of redshift, gravitational time dilation, and other effects have all been found to precisely match the predictions of general relativity.
[04] What are the different components of the current universe?
- Today, the universe is composed of:
- 0.008% radiation (photons)
- 0.1% neutrinos
- 4.9% normal matter
- 27% dark matter
- 68% dark energy
- The expansion rate and evolution of the universe is determined by the relative amounts of these different energy components.
[05] How do the different energy components affect the expansion of space?
- For radiation, the "space stretches" analogy works well, as the wavelength of light increases with the expansion.
- For dark energy, which has a constant energy density, the "creation of new space" analogy is more appropriate, as the total dark energy increases as the volume expands.
- Neither analogy works universally - they each capture aspects of how different energy forms interact with the expanding spacetime.
Shared by Daniel Chen ·
© 2024 NewMotor Inc.