America & China's Chip Race
🌈 Abstract
The article discusses the U.S. government's efforts to secure a domestic semiconductor supply chain and limit China's ability to build out its own semiconductor manufacturing capabilities. It covers the following key points:
- The U.S. has implemented a two-pronged strategy - providing subsidies to incentivize domestic chip manufacturing through the CHIPS Act, and imposing sanctions and export restrictions to limit China's access to advanced semiconductor technology and equipment.
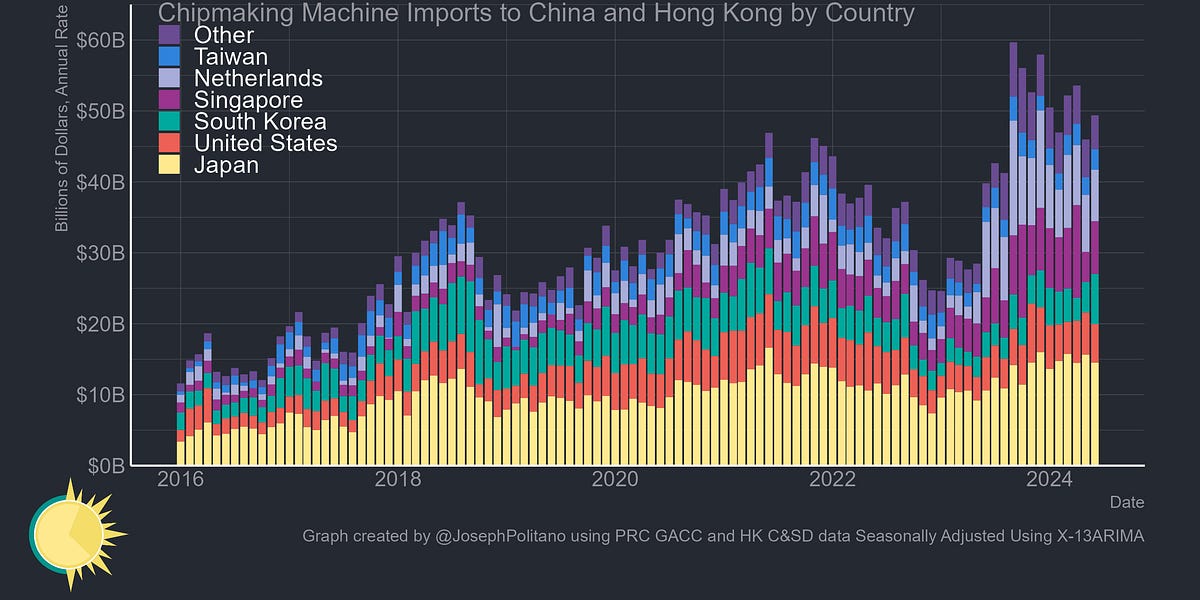
- Despite these efforts, China has continued to rapidly build out its own semiconductor manufacturing capabilities by importing record amounts of chipmaking equipment from countries like Japan, the Netherlands, and others.
- The U.S. efforts have accelerated China's push to develop its own semiconductor supply chain, heightening the stakes in the geopolitical rivalry between the two countries.
- While the U.S. is seeing some gains in domestic chip production and manufacturing capacity, it still lags far behind China in terms of investment and imports of semiconductor equipment.
🙋 Q&A
[01] U.S. Government's Semiconductor Strategy
1. What are the two prongs of the U.S. government's strategy to secure a domestic semiconductor supply chain?
- The first prong is providing subsidies and incentives through the CHIPS Act to encourage semiconductor manufacturers to build new fabrication facilities in the U.S.
- The second prong is implementing sanctions and export restrictions to limit China's access to advanced semiconductor technology and equipment.
2. How have China's efforts to build out its own semiconductor manufacturing capabilities responded to the U.S. strategy?
- China has continued to rapidly import record amounts of semiconductor manufacturing equipment from countries like Japan, the Netherlands, and others, despite the U.S. sanctions and export controls.
- This has accelerated China's push to develop its own independent semiconductor supply chain, heightening the geopolitical rivalry between the U.S. and China.
3. How do the U.S. and China's semiconductor manufacturing buildouts compare?
- While the U.S. is seeing some gains in domestic chip production and manufacturing capacity through the CHIPS Act, it still lags far behind China in terms of investment and imports of semiconductor equipment.
- China's investment in fixed assets for computer and electronics manufacturing has been growing at a much faster pace than the U.S.
[02] Impact on Global Semiconductor Supply Chains
1. How have the U.S. efforts impacted Taiwan's "silicon shield" geopolitical defense?
- The increase in China's domestic chip production, coupled with the sanctions limiting access to the highest-end foreign semiconductors, has put a lid on China's chip imports.
- This is slowly weakening Taiwan's geopolitical defense afforded by its control over high-end chip manufacturing that Chinese (and global) supply chains depend on.
2. How have the U.S.-China semiconductor tensions impacted global semiconductor trade and equipment production?
- American orders for Taiwanese semiconductors have risen significantly, making the U.S. now Taiwan's most important customer, surpassing China.
- Output of semiconductor equipment in key manufacturing nations like the Netherlands and Japan has held at or near their all-time highs despite a post-2022 slowdown, benefiting from the semiconductor industry "gold rush".
3. How do you see the U.S.-China semiconductor competition evolving going forward?
- The U.S.-China competition in the semiconductor industry is likely to only intensify further, with neither country feeling they have an off-ramp to the ongoing escalation cycle.
- This will force companies and countries in the semiconductor supply chain to increasingly choose sides between the U.S. and China.