Worldwide divergence of values - Nature Communications
🌈 Abstract
The article examines the debate around cultural change in a modernizing and globalizing world. It tests the competing predictions of cultural convergence versus divergence by analyzing survey data from 76 national cultures over the period 1981-2022. The key findings are:
- There is evidence of global value divergence, especially for values emphasizing tolerance and self-expression, with a growing gap between high-income Western countries and the rest of the world.
- Countries with similar per-capita GDP levels have held similar values over the last 40 years.
- Over time, geographic proximity has emerged as an increasingly strong correlate of value similarity, indicating that values have diverged globally but converged regionally.
🙋 Q&A
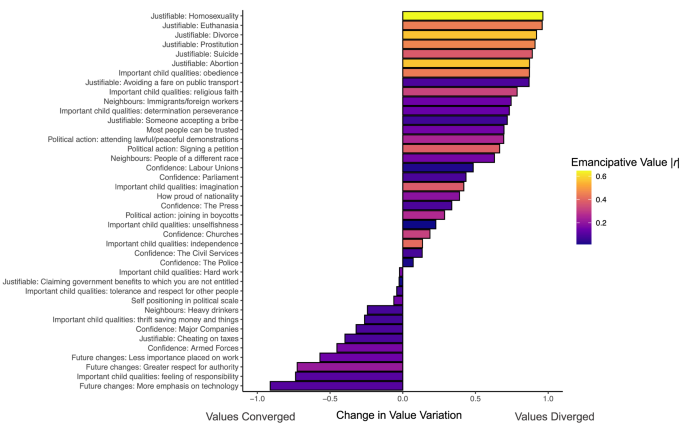
[01] Value Divergence at the Item Level
1. What did the analysis of value variation across the 40 survey items show? The analysis found strong evidence of value divergence over time. A mixed effects model showed that timepoint was significantly associated with greater value variation across the 40 items. Replicating this using correlations between timepoint and value variation for each item, 27 out of 40 items showed divergence over time.
2. Which types of values showed the highest rates of divergence? The rate of value divergence was correlated with the items' loading on Welzel's "emancipative vs. obedient" values dimension, but not the "sacred vs. secular" dimension. The 7 items with the highest divergence scores were related to tolerance of individual expression versus emphasis on group obedience, such as justifiability of homosexuality, euthanasia, divorce, and abortion.
3. Can you provide some examples of how values have diverged between Western and non-Western countries over time? The article provides the example of Australia and Pakistan. In the 1980s, their views on the importance of childhood obedience and the justifiability of divorce were relatively similar. But over time, Australia endorsed more emancipative values while Pakistan remained more traditional, leading to a growing divergence.
[02] Value Divergence at the Country Level
1. What did the analysis of value distinctiveness at the country level find? The analysis found that value distinctiveness has been rising over time, indicating that countries have diverged in their values. This effect held even when controlling for potential confounds like changing sample composition over time.
2. Which country characteristics predicted greater value similarity between countries? The key predictor of value similarity was GDP per capita - higher-income countries tended to have more distinctive values compared to lower-income countries. In contrast, other factors like inequality, globalization, and political rights did not significantly predict value similarity.
3. How did the relationship between wealth and value distinctiveness vary across regions? The positive relationship between wealth and value distinctiveness was strongest in Europe, but significantly weaker or non-significant in Asia and Africa. This suggests that rising wealth has led to value divergence in Western countries, but not necessarily in non-Western regions.
[03] Within-Country Heterogeneity and Value Distinctiveness
1. What was the relationship between within-country heterogeneity and value distinctiveness? Countries with more homogeneous values within their populations tended to be more distinctive from the rest of the world, while countries with more heterogeneous values were more similar to global norms. This suggests that as countries develop more consensus around values, they may become more unique compared to the global average.
2. What are the implications of this finding for understanding cultural change? The authors suggest this finding may help explain why some high-income Western countries have developed very distinctive values - their citizens have converged around certain emancipative values, making them more different from the global average. In contrast, more diverse countries may struggle with internal divisions but end up more similar to global norms when averaged across their population.
[04] Predictors of Value Similarity Over Time
1. What were the key predictors of value similarity between countries over time? The analysis found that geographic proximity and religious similarity became increasingly strong predictors of value similarity between countries over time. In contrast, factors like inequality and political rights did not significantly predict value similarity.
2. How does this relate to theories of cultural change and globalization? The findings support the idea that globalization has led to value divergence globally, but value convergence regionally, as countries in close geographic and religious proximity have developed more similar values over time. This is consistent with theories like Huntington's "clash of civilizations" thesis, which predicted a resurgence of cultural divides based on historical religious and linguistic differences.
</output_format>