What LLM-powered Products Are Worth Developing? UX and Adoption Perspectives
🌈 Abstract
The article discusses which GenAI (Generative AI) product ideas are worth exploring, focusing on user behavior and the unique features of large language models (LLMs). It analyzes the success factors for different types of GenAI applications, including those with high quality standards, specialized AI copilots, and applications that seamlessly integrate LLMs into familiar workflows. The article also suggests that new GenAI products are better suited for a B2B2C (Business-to-Business-to-Consumer) model rather than a direct B2C (Business-to-Consumer) approach.
🙋 Q&A
[01] Applications With High Quality Standards or Costly Quality Monitoring May Fail 🚫
1. What are the key challenges with LLM-based applications that have high quality standards or require costly quality monitoring?
- LLM outcomes are unpredictable and difficult to evaluate, as different user groups or contexts may evaluate the product very differently, and the results can degrade over time as the knowledge base expands.
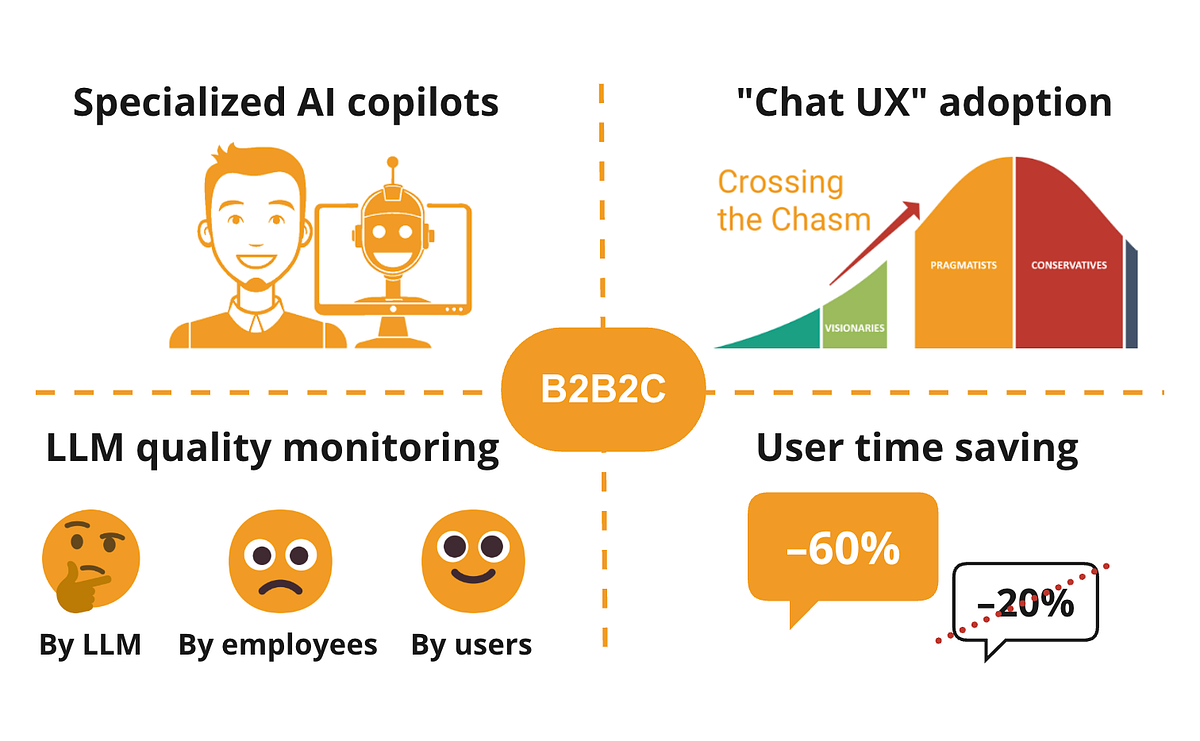
- Monitoring the performance (quality) of an LLM-based application is crucial for its success, but it can be difficult to achieve, as model-graded evaluation may not provide enough error prevention.
- The success of an LLM-based application depends on the users' tolerance for errors. If the error tolerance is low, the application may fail unless the cost of personnel required to fix LLM errors is justified by the product's profitability.
[02] Specialized Copilots Are in Demand ✅
1. Why are specialized AI copilots more promising than general-purpose AI assistants?
- LLMs lack systems thinking and a comprehensive understanding of broader contexts, often struggling with rare situations outside their data and prompt coverage. This makes human review of LLM outputs necessary, which is better suited for users serving as evaluators rather than the development company's employees.
- Specialized copilots that can assist professionals in specific fields more effectively than general-purpose AI assistants have a higher potential for success, as they can offer a substantially higher value proposition to their target user groups.
2. What are the key features that make a specialized copilot successful?
- The copilot should reflect the unique expertise and teaching style of the target user (e.g., a trainer or course creator).
- The copilot should be capable of generating various content formats beyond just text, such as learning materials and student assignments.
- The copilot should seamlessly integrate with the user's existing tools and workflows, rather than requiring them to rely on copy-pasting the copilot's results.
[03] Marginal Effort-Saving Apps Don't Cut It 🚫
1. Why are users resistant to changing their habits when adopting new AI-powered applications?
- Users are often resistant to changing their habits, whether consciously or subconsciously, and the advantages of "conversational UX design" and LLM-based "personalization" and "adaptation to user needs" can be unpredictable and annoying.
- The chat-based interface and iterative improvements required to get quality LLM outputs can be challenging for typical users accustomed to simple point-and-click interactions.
2. What level of efficiency gains are required for users to adopt new AI applications?
- Mere incremental time savings in the range of 10-30% are not a sufficient incentive for users to adopt a new application, as they are resistant to changing their established habits.
- To overcome this inertia, the efficiency gains need to be transformative, not just marginal improvements, but multifold reductions in effort.
- It's better for the application to empower users to become the person they've always aspired to be, rather than just saving them time.
[04] Applications "Smartly" Integrating LLMs into Familiar Workflows Are in Demand ✅
1. What are the key factors for successfully integrating LLM capabilities into a product?
- The integration should create a 'whole product' that seamlessly blends LLM functionalities with other features, addressing user needs end-to-end.
- The integration should be 'smart', requiring users to do nothing new to benefit from the AI capabilities, and should simply enhance the user's current experience without adding new steps or options.
- Simplicity, ease of use, and product completeness are crucial factors in crossing the 'chasm' between early adopters and the mainstream market.
2. What are some examples of successful LLM integration into existing products?
- In an educational app, AI-generated personalized content or assignments could be triggered by the user's familiar "Next" button, without them noticing the AI integration.
- Integrating AI actions into existing app menus, rather than as standalone chat assistants, can improve adoption, though not as much as the seamless integration approach.
[05] New GenAI Products Are Better Suited to B2B2C than B2C
1. Why are new GenAI products better suited for a B2B2C (Business-to-Business-to-Consumer) model rather than a direct B2C (Business-to-Consumer) approach?
- In a B2C context, the challenges of data and privacy, as well as the insurmountable advantage of tech giants, make it difficult for startups to succeed with new GenAI products.
- In a B2B2C model, quality data can come from the B2B clients rather than individual B2C customers, and the LLM-powered product can help the B2B clients boost profitability or reduce the cost of service delivery for their own customers.
- B2B clients typically have highly motivated users, which is easier to overcome the weaknesses of LLM-based applications, such as unfamiliar and complicated user experiences, compared to the B2C market.