Why Is 80% of Mexico Nearly Empty?
🌈 Abstract
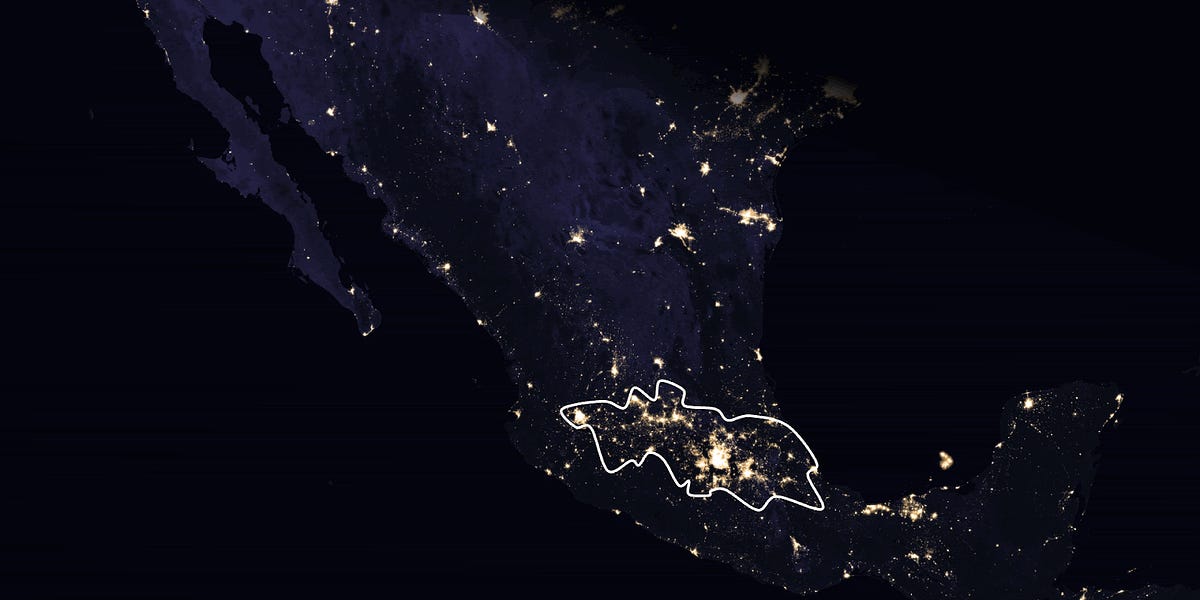
The article explores the reasons behind the high population density in the central regions of Mexico, particularly the Mexican heartland, and how this geographic and environmental context has shaped the development of Mexican civilization, including the rise of the Aztec Empire and the construction of the famous Mexican pyramids.
🙋 Q&A
[01] Reasons for High Population Density in the Mexican Heartland
1. What are the key factors that have contributed to the high population density in the central regions of Mexico?
- The central regions of Mexico, known as the Mexican heartland, have a high population density due to several favorable environmental and geographic factors:
- Mild, stable temperature throughout the year due to the high altitude of the region
- Adequate rainfall and water supply from the surrounding mountains and endorheic basins (closed drainage systems)
- Fertile volcanic soil (andisols) that is highly productive for agriculture
- Flat, plateau-like terrain created by the accumulation of sediments from the mountains over millions of years
- The presence of lakes and inland water bodies that provided water, transportation, and other resources
2. How did the Aztecs and other pre-Hispanic civilizations take advantage of these geographic and environmental conditions?
- The Aztecs and other Mesoamerican civilizations were able to thrive in the Mexican heartland due to the region's favorable conditions:
- The Aztecs built their capital, Tenochtitlan, on an island in Lake Texcoco, which they engineered to have a freshwater supply for irrigation and agriculture
- The fertile volcanic soil and mild climate allowed the Aztecs to cultivate up to 7 harvests per year, supporting a large population
- The lakes and rivers provided transportation, fish, and other resources that were crucial for the Aztec Empire
[02] Role of Volcanoes and Tectonic Plates
1. What is the connection between the volcanoes in the Mexican heartland and the region's suitability for human settlement?
- The volcanoes in the Mexican heartland, which are the result of the subduction of the Cocos Plate under the North American Plate, have played a crucial role in shaping the region's environment:
- The volcanoes have raised the elevation of the area, creating a mild, stable climate despite the region's tropical latitude
- The volcanic activity has also produced highly fertile andisol soils, which are ideal for agriculture
- However, the Aztecs and other civilizations had to contend with the threat of volcanic eruptions, which could have been both destructive and beneficial (e.g., providing water and sediments)
2. How did the tectonic plate movements and volcanic activity in the region contribute to the development of the Mesoamerican civilizations?
- The tectonic plate movements and resulting volcanic activity in the Mexican heartland were instrumental in creating the favorable environmental conditions that allowed Mesoamerican civilizations to thrive:
- The subduction of the Cocos Plate under the North American Plate raised the elevation of the region, leading to a mild, stable climate and the formation of fertile volcanic soils
- The volcanoes and mountains in the region captured rainfall and created endorheic basins, providing a reliable water supply for agriculture and human settlement
- The Aztecs and other civilizations were able to take advantage of these environmental conditions to build their cities and empires, with the Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan being one of the largest and most populous cities in the world at the time.