Why Startups Fail & What We Can Learn From It
🌈 Abstract
The article discusses the key reasons why startups fail, based on insights from various research studies. It covers the top 3 reasons for startup failure: no/bad business model, lack of business development, and running out of cash. The article also explores how startups can successfully pivot to overcome these challenges and increase their chances of success.
🙋 Q&A
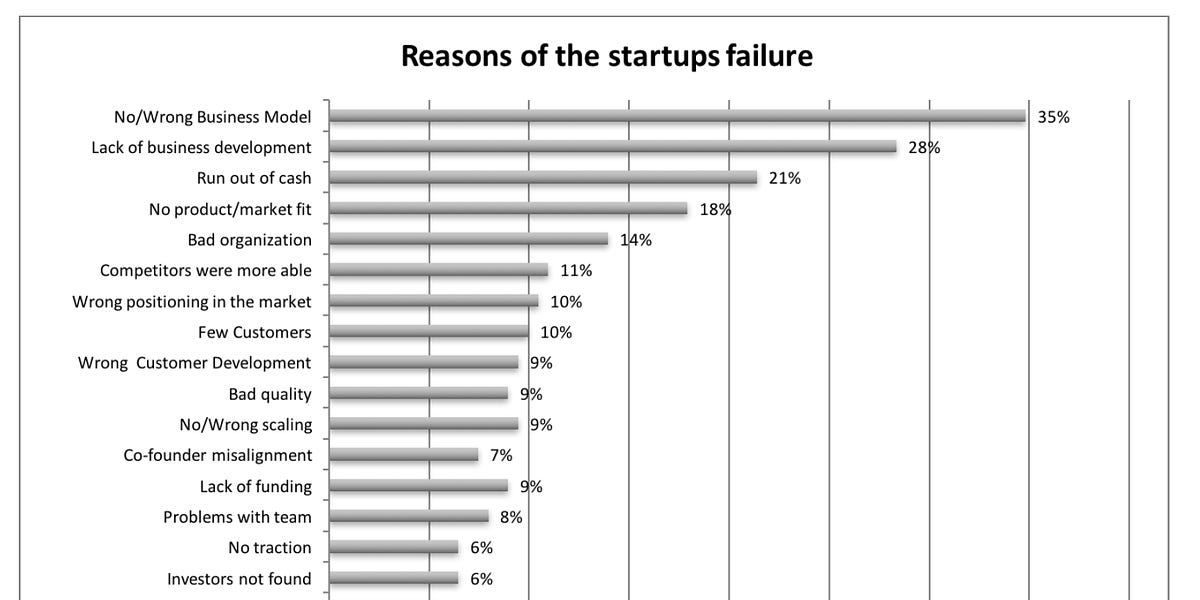
[01] Top 3 Reasons for Startup Failure
1. What are the top 3 reasons for startup failure according to the article? The top 3 reasons for startup failure are:
- No/Bad Business Model: Startups often fail due to a flawed or non-existent business model, including poor market positioning, lack of product/market fit, and deficient customer development efforts.
- Lack of Business Development: Startups fail due to the absence of a well-thought-out business development strategy, leading to issues like reliance on untested assumptions, overlooking customer engagement and feedback loops, and neglecting competitive analysis.
- Running Out of Cash: Startups fail due to misalignment between cash inflows and outflows, including underestimating initial capital requirements, ineffective cash flow management, and growth mismanagement.
2. What key insights does the article provide about these top 3 reasons for startup failure?
- For the "No/Bad Business Model" reason, the article highlights that more than a third of failed startups suffered from a failure to adapt the business model based on market feedback, misunderstanding of product-market fit, and inadequate customer segmentation efforts.
- For the "Lack of Business Development" reason, the article emphasizes that reliance on untested assumptions and not iterating quickly enough on feedback and data played a substantial role in 28% of startup failures.
- For the "Running Out of Cash" reason, the article notes that startups often falter not just from a lack of market demand but from financial missteps, including underestimating the initial capital needed, premature scaling, and mismanaging cash flows, which caused 21% of failed startups.
[02] Pivoting as a Solution
1. How can pivoting help startups overcome the challenges they face? The article discusses how pivoting can be a solution for startups facing challenges. It highlights examples of successful pivots, such as Instagram, Slack, Twitter, and Shopify, where startups transformed their original ideas and business models to adapt to market demands or technological opportunities.
2. What are the key principles and frameworks for successful pivoting according to the article? The article outlines two core principles for successful pivoting:
- Validated learning from failure: Startups should use the "lean startup" approach to continuously test their business model hypotheses against market realities and learn from both successes and failures.
- Astute observation of customer behaviors: Startups should focus on refining their value proposition to meet unmet or evolving customer needs, as evidenced by the prevalence of "customer-need" pivots.
The article also presents a framework for the pivot process, which includes four stages: recognition, generating options, seizing and testing, and reconfiguration. This framework emphasizes the importance of involving stakeholders throughout the pivot process to maintain trust and support.
3. How can startups determine the right timing for a pivot? The article suggests that startups can use the Lean Startup Framework and monitor their product's retention curve to help determine the right timing for a pivot. It notes that building MVPs and iterating quickly, especially in the early stages, is the best way to pick up on pivot signals. Later in the maturity cycle, more structured processing of feedback is necessary to identify the right time to pivot.